How To Manage Chronic Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
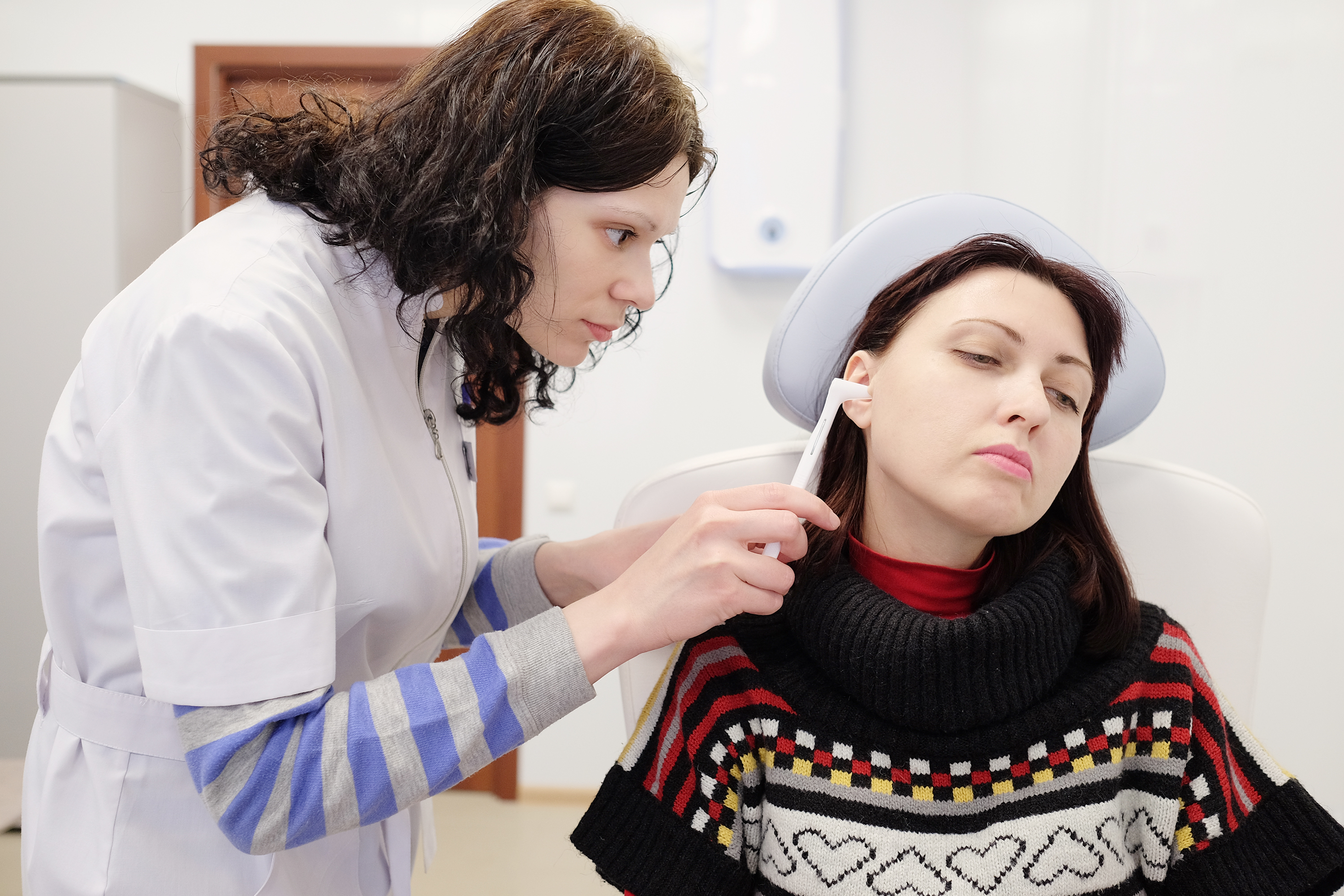
We all experience eustachian tube dysfunction at some point in our lives, usually during a respiratory virus. Ear pressure, a sense of fullness in the ears, or muffled hearing can last for a week or so and then vanish when the illness clears up on its own.
But for people with chronic eustachian tube dysfunction, these symptoms don’t clear up. They persist for a month or more, even when everything else in the body seems to be working well.
So what is chronic eustachian tube dysfunction? How do you know if you have it? And if you do have it, what can you do to treat it?
What Is Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
The eustachian tubes are tiny tubes made of bone and cartilage that run from the middle ear to the back of the nose. The eustachian tubes stay closed at rest, and they open when you swallow, chew, or yawn.
The eustachian tubes’ opening and closing action helps to equalize the air pressure in your middle ear with the air pressure around you. This is why yawning or chewing gum helps to relieve that feeling of ear pressure on an airplane. Eustachian tubes also drain fluid from the middle ear to the back of the nose and down the throat.
When the eustachian tubes are functioning normally, you won’t notice anything about them. But if a eustachian tube becomes blocked, fluid and pressure build up in the middle ear. This is called eustachian tube dysfunction and can lead to a host of unpleasant symptoms.
Causes of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Eustachian tube dysfunction most often arises from swelling in the nose and excess mucus production caused by allergies, sinus infection, or a respiratory virus. This blocks off the entrance of the eustachian tube, leading to dysfunction.
Altitude and pressure changes from flying on an airplane, SCUBA diving, or driving on mountain roads can also cause eustachian tube dysfunction, though this is usually temporary and resolves within minutes or hours.
Smoking can irritate the eustachian tube and lead to dysfunction.
In children under the age of three or four, the eustachian tubes are much shorter and more horizontal than they will be later in life. This makes it incredibly easy for fluid from the nose to drain into the ear and become trapped, causing frequent ear infections. The adenoids, a patch of lymphatic tissue in the back of the nose, can also swell and block the eustachian tubes in young children.
Symptoms of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Symptoms of eustachian tube dysfunction vary, but can include:
- Feeling of fullness in the ears.
- Muffled sound, as if hearing underwater.
- Painful pressure.
- Ringing in the ears.
- Loss of balance.
- Popping or fluttering sensation in the ears.
What Makes Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Chronic?
Everyone experiences eustachian tube dysfunction from time to time on a cross-country flight or during a cold or flu. But if you’re experiencing symptoms constantly for no obvious reason, this is chronic eustachian tube dysfunction, and it needs treatment.
Treatment Options for Chronic Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Symptoms of acute (not chronic) eustachian tube dysfunction usually resolve on their own, but if you’re experiencing long-term symptoms of eustachian tube dysfunction, talk with your ENT doctor about medical intervention.
At-Home Treatment
In our office, we start by trying the least invasive treatment option first: medications to decrease the inflammation in your nose.
Antihistamines (like Claritin, Zyrtec, Xyzal, or Allegra) can help decrease the swelling in the nose, which may help to unplug your eustachian tubes. Decongestants and topical steroid sprays may also provide relief from your symptoms. These medications are available over the counter at your local pharmacy or grocery store.
For relief during this stage, a technique called autoinsufflation may help to clear the eustachian tube and release some of that pressure in the middle ear. To try this technique, pinch your nose and exhale gently through your mouth while the mouth is closed.
Myringotomy and Tympanostomy
If the symptoms don’t resolve after about a month, you likely have chronic eustachian tube dysfunction. At this point, your ENT doctor may suggest a myringotomy or tympanostomy.
A myringotomy is a simple in-office procedure. Your ENT surgeon uses a sharp tool to make a small hole in the eardrum. This allows the middle ear to drain and ventilate through the outer ear. The eardrum will repair itself within about two weeks, so this is only a short-term solution to the problem.
If the myringotomy is helpful, a tympanostomy tube can be placed in the eardrum hole that the ENT doctor created. This tube is about a millimeter in diameter and prevents the eardrum from closing up. This “release valve” bypasses the eustachian tube altogether, continually allowing fluid to drain through the outer ear and keeping air pressure equalized.
Eustachian Tube Balloon Dilation
Eustachian tube balloon dilation is another simple office procedure. Balloon dilation involves very little pain or risk, and has a very high success rate. Because the balloon is inserted through the nostrils, there isn’t any scarring to worry about.
In eustachian tube balloon dilation, an ENT surgeon thoroughly numbs the back of your nose where the eustachian tube empties. The surgeon then inserts a small balloon into the eustachian tube and simply inflates it.
This inflation opens up the part of the eustachian tube that tends to collapse. Once the balloon is properly pressurized, it remains inflated for about two minutes. Then the balloon is deflated and removed.
The effects of a balloon dilation aren’t permanent, but research continues to show consistent improvement in eustachian tube function for one year or longer.
Dealing With Chronic Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
At ENT Associates of Lubbock, we see patients with eustachian tube dysfunction every day. Our team has extensive experience with this problem and knows how to help alleviate its irritating symptoms. Get in touch with us today to schedule a consultation. We look forward to hearing from you!
Dr. Cuthbertson is a physician at Ear Nose & Throat Associates of Lubbock. He joined the team at ENT Lubbock from Houston, where he was chief resident of the prestigious Bobby R. Alford Department of Otolaryngology at Baylor College of Medicine. He is board certified in Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery and has quickly built a reputation, not only as an extremely skilled surgeon, but as an approachable and compassionate clinician adept in the newest standards and technologies. Learn more about Dr. Cuthbertson.
Categories: